The Belt and Road Initiative: China's Global Development Strategy
The Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), also known as One Belt One Road (OBOR), is one of the most ambitious infrastructure and economic development projects in modern history. Proposed by Chinese President Xi Jinping in 2013, the initiative aims to enhance global trade and stimulate economic growth across Asia, Africa, Europe, and beyond through large-scale investments in infrastructure, transportation, energy, and digital connectivity.
What Is the Belt and Road Initiative?
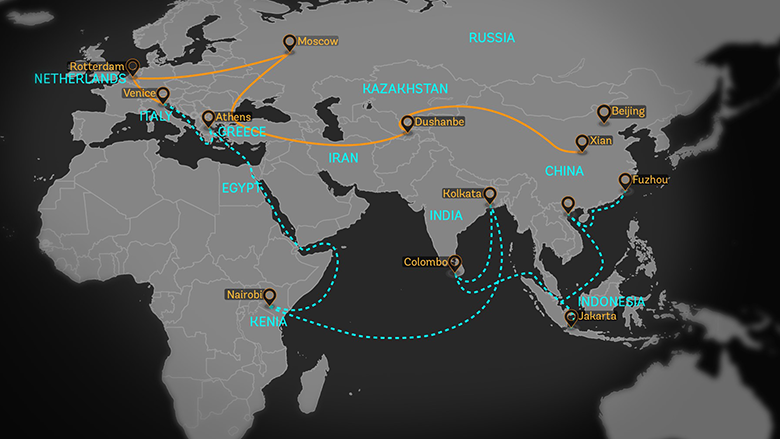
At its core, the Belt and Road Initiative is a global development strategy adopted by the Chinese government. It focuses on building trade routes that mirror the ancient Silk Road and Maritime Silk Road, aiming to connect China to the rest of the world through land and sea.
The initiative includes two major components:
The Silk Road Economic Belt – a land-based route connecting China with Central Asia, Russia, and Europe.
The 21st Century Maritime Silk Road – a sea-based route linking China with Southeast Asia, Africa, the Middle East, and Europe.
Together, these routes form a vast network that facilitates international trade, investment, and cooperation on a scale never seen before.
Historical Roots: Inspired by the Ancient Silk Road
The concept behind the Belt and Road Initiative is deeply rooted in China’s history. The ancient Silk Road was a network of trade routes connecting East and West from the 2nd century BCE to the 14th century CE. Goods, technologies, cultures, and religions flowed across continents, making China a central hub in the world’s early globalization.
By referencing the Silk Road, the BRI draws on this historical legacy, positioning China once again at the crossroads of global trade and diplomacy.
Goals of the Belt and Road Initiative
The Belt and Road Initiative is not just about building roads and railways. It has broader goals that reflect China’s long-term strategic and economic interests. These include:
Infrastructure Development: Building highways, railways, ports, and airports to improve connectivity between countries.
Trade Expansion: Facilitating the flow of goods and services by removing trade barriers and improving logistics.
Financial Integration: Encouraging investment through institutions like the Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB).
Cultural Exchange: Promoting mutual understanding and cooperation through people-to-people connections.
Energy Security: Developing pipelines, power plants, and energy corridors to meet growing energy demands.
Countries Involved in the BRI
As of 2025, over 150 countries and international organizations have signed agreements or expressed support for the Belt and Road Initiative. This includes nations across Asia, Africa, Europe, Latin America, and even the South Pacific. Key participant countries include:
Pakistan (China-Pakistan Economic Corridor)
Kenya and Ethiopia (rail and port infrastructure)
Greece (Port of Piraeus)
Italy (first G7 country to join)
Indonesia, Malaysia, and Sri Lanka (maritime projects)
Each country participates in ways that reflect its own development needs and geopolitical interests.
Major Projects and Achievements
The BRI has already seen the completion of many high-profile infrastructure projects. Some of the most significant include:
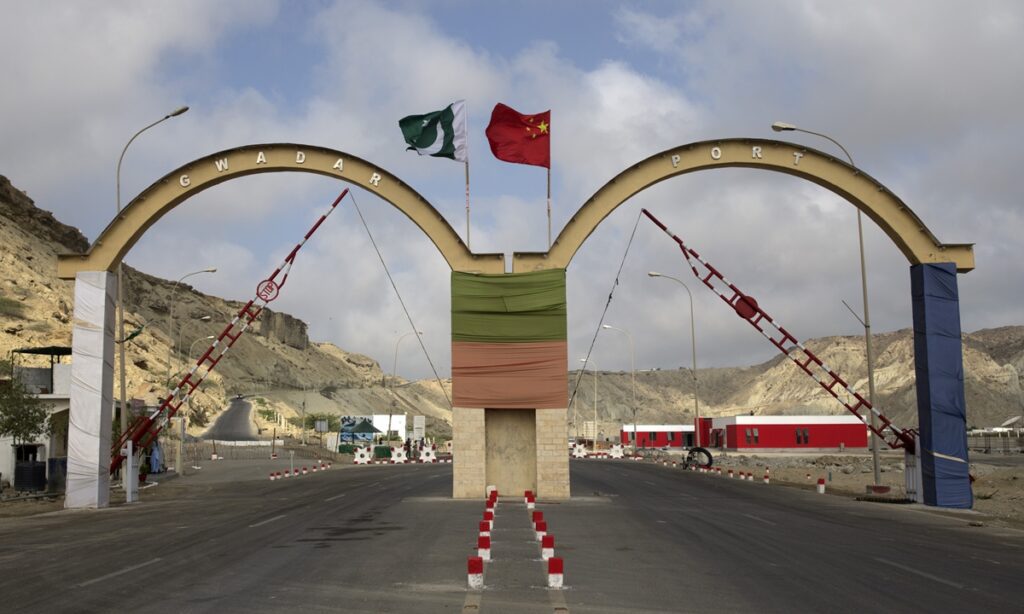
1. China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC)
One of the flagship projects of the BRI, the CPEC connects Gwadar Port in Pakistan to China’s Xinjiang region. It includes highways, railways, power plants, and special economic zones.

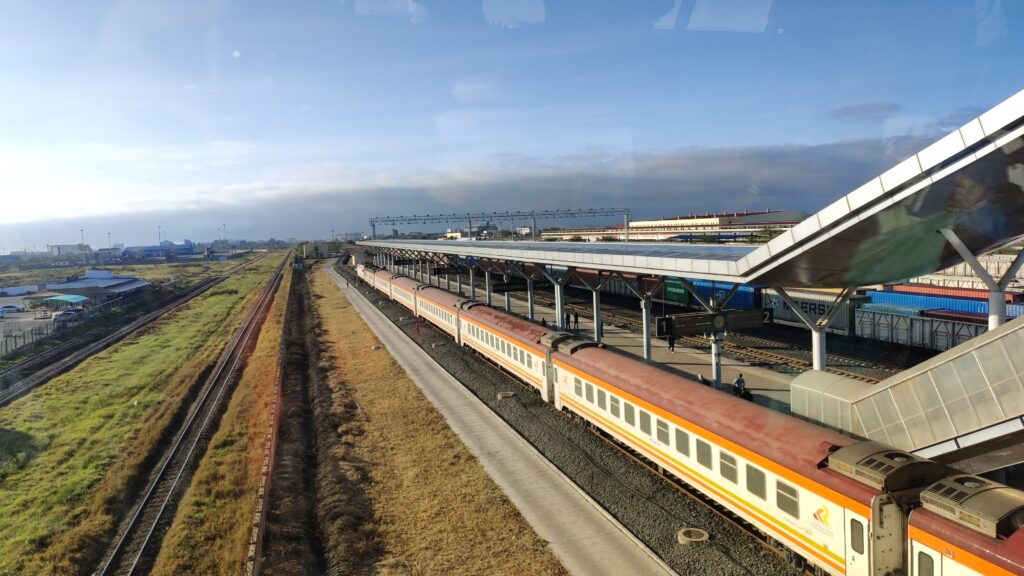
2. Mombasa-Nairobi Railway (Kenya)
This major railway project, completed in 2017, connects Kenya’s capital Nairobi with the port city of Mombasa, drastically reducing travel time and enhancing trade.

3. Port of Piraeus (Greece)
The Port of Piraeus is the largest port in Greece and one of the largest in Europe. Acquired by China’s COSCO Shipping, the Port of Piraeus has become a major entry point for Chinese goods into Europe, thanks to its strategic location.

4. Jakarta-Bandung High-Speed Railway (Indonesia)
The first high-speed railway in Southeast Asia, completed with Chinese support, this project has reduced travel time between the two major Indonesian cities to under an hour.
Economic and Strategic Impact
The Belt and Road Initiative has significantly enhanced China’s global influence. By investing in infrastructure abroad, China strengthens diplomatic ties and opens new markets for Chinese companies. For participating countries, the BRI often brings much-needed infrastructure and investment.
However, the initiative also faces criticism:
Debt sustainability concerns, as some nations struggle to repay Chinese loans.
Geopolitical tensions, especially with the U.S. and India, who see the BRI as a tool for Chinese expansion.
Environmental and social impacts, with some projects disrupting local communities and ecosystems.
Despite these challenges, the BRI remains a cornerstone of China’s foreign policy and economic diplomacy.
The Digital Silk Road
In recent years, the BRI has expanded beyond physical infrastructure to include digital connectivity. The Digital Silk Road focuses on building internet infrastructure, smart cities, e-commerce platforms, and satellite networks. It aims to connect developing nations to the global digital economy, while also promoting Chinese tech companies abroad.
Key aspects of the Digital Silk Road include:
Undersea fiber-optic cables
5G networks
Smart city technologies
E-commerce platforms like Alibaba and JD.com
The Belt and Road in the Future
Looking forward, the Belt and Road Initiative is expected to evolve to address new global challenges. These include:
Green development: Promoting environmentally sustainable projects.
Health cooperation: Enhancing global public health systems post-COVID-19.
Industrial modernization: Supporting digital transformation and industrial upgrading in partner countries.
China has also pledged to make the BRI more transparent, inclusive, and sustainable, in response to international concerns.
Conclusion: Why the Belt and Road Initiative Matters
The Belt and Road Initiative is more than a development project—it is a strategic vision for reshaping the global economic landscape. It reflects China’s ambitions to lead in global trade, diplomacy, and innovation.
For countries along the Belt and Road, the initiative offers opportunities for growth, partnership, and modernization. For the rest of the world, it represents a new model of international cooperation—one that is reshaping 21st-century geopolitics and commerce.
At China Analysis, we continue to monitor the Belt and Road Initiative and its far-reaching implications. Stay tuned for ongoing updates, insights, and expert analysis on China’s evolving role in the world.





